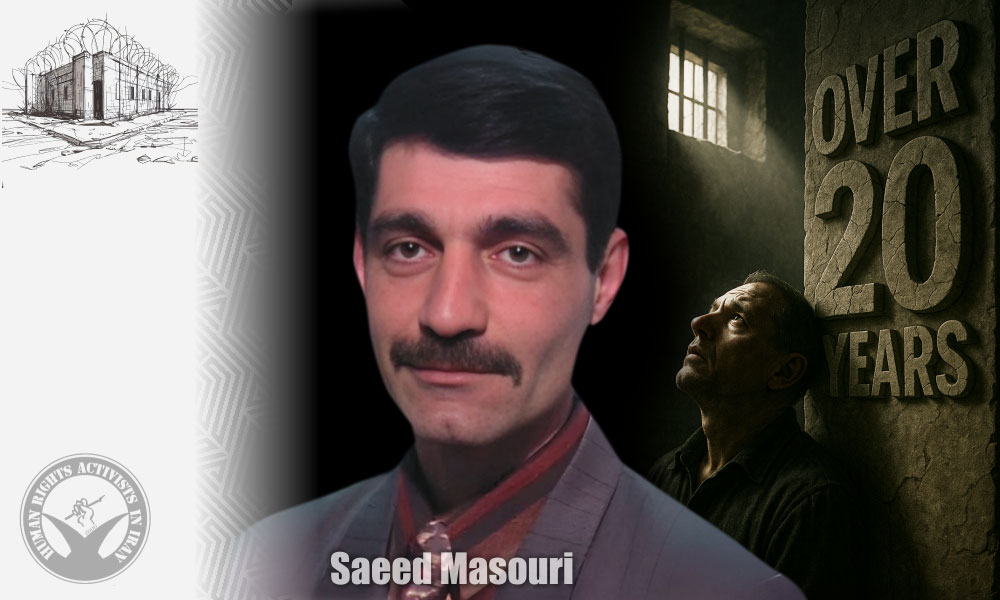
HRANA – Numerous political and religious prisoners in Iran have spent more than two decades in detention. To ensure their stories are not lost amid the constant churn of daily news, HRANA publishes a series of reports dedicated to them. Each report reviews the prisoner’s case history, prison conditions, access to basic rights, and urgent needs.
This report examines the current situation of Afshin Baymani after over two decades in prison.
Information Sheet
• Name: Afshin Baymani
• Year of Arrest: 2000 (1379 in the Iranian calendar)
• Stated Charge: “Moharebeh [enmity against God] through collaboration with the People’s Mojahedin Organization of Iran (PMOI/MEK)”
• Initial Sentence: Death penalty
• Current Sentence: Life imprisonment (commuted with one degree of reduction)
• Places of Detention:
After his conviction, Baymani spent years in various wards of Rajai Shahr Prison in Karaj. In August 2023, he was transferred from there to Ward 10 (Section 8) of Evin Prison, without respect for the principle of separation of crimes. In September of the same year, again without separation of crimes and with violence, he was transferred from Evin to the security ward (Unit 3) of Ghezel Hesar Prison in Karaj. In November 2023, he was granted medical furlough from Ghezel Hesar for treatment and care. However, after about one month—despite incomplete treatment—he was rearrested at his residence by police forces on the orders of the Head of Enforcement of Verdicts of Karaj Revolutionary Court and transferred to Asadabad Prison in Mobarakeh, Isfahan, where he was held in the health ward. In January 2024, he was once again transferred from Asadabad to Ghezel Hesar Prison, where he remains to this day.
• Leave / Access: No furlough has been reported in recent years; access to family and lawyer has been limited.
• Current Status: Still serving a life sentence despite legal changes that could allow for review or reduction.
Case Background and Judicial Process
Afshin Baymani was arrested on September 5, 2000, on charges of “Moharebeh through collaboration with the PMOI” and allegedly assisting his brother, Mehdi Baymani, a member of the PMOI, to escape. He was sentenced to death by the Tehran Revolutionary Court, and this ruling was upheld on appeal. After six years, his sentence was commuted to life imprisonment. While this change prevented his execution, it placed him in the category of indefinite imprisonment, which in practice can last for decades and significantly restricts access to review mechanisms.
Key Points in the Judicial Process
• Severe Security Charge: The “Moharebeh” charge is among the most serious in Iran’s political-security cases, with broad legal and practical consequences.
• Sentence Conversion: His initial death sentence and subsequent commutation to life highlight both the severity of the charge and later judicial interventions, though without resolving potential injustices in due process.
• Continued Imprisonment Despite Legal Changes: Legal reforms allowing retrials, sentence reductions, or conditional release in such cases have not been applied to Baymani.
Detention Conditions and Transfers
Throughout his imprisonment, Baymani has been repeatedly transferred between prisons and wards, including Rajai Shahr, Evin, Ghezel Hesar, and Asadabad Prison. Transfers were often violent and carried out without regard to the separation of crimes. He has repeatedly protested mistreatment, lack of medical care, and inhumane conditions, including hunger strikes in 2011 and 2018.
Observations on Prison Standards
• Frequent Transfers: Repeated relocations disrupted family contact, legal representation, and medical treatment.
• Solitary Confinement as Punishment: Baymani has been held in solitary on numerous occasions, sometimes for weeks, in violation of international standards that require solitary to be rare and tightly controlled.
• Violence in Prison: Reports document multiple instances of physical and verbal abuse by prison authorities, including beatings during transfers and threats during hunger strikes.
• Denial of Medical Care: Despite suffering from heart disease, blocked arteries, chest pain, hypertension, diabetes, kidney stones, and requiring angiography and mitral valve surgery, he has repeatedly been denied hospital access. This deliberate deprivation violates the right to health and, in some cases, the right to life, and is often used as a form of pressure.
Access to Family, Lawyer, and Leave
In recent years, Baymani has not been granted furlough. Reports indicate limited access to both family and lawyer, restricting not only his well-being but also his ability to pursue legal remedies.
Potential Legal Pathways (General Recommendations)
1. Retrial: Exploring new evidence or procedural flaws.
2. Sentence Reduction or Commutation: If legal grounds allow.
3. Conditional Release / Suspension of Sentence: Based on duration served, conduct, and medical condition.
4. Addressing Rights Violations: Including access to medical care, protection from abuse, family visits, and legal counsel.
5. International Documentation and Advocacy: If domestic channels remain blocked.
Timeline Summary
• 2000 (1379): Arrest; charged with Moharebeh through collaboration with the PMOI
• Initial Sentence: Death penalty commuted to life imprisonment
• 2000s–2020s: Years spent in Rajai Shahr Prison; repeated transfers
• 2011–2016: Several hunger strikes, solitary confinements, violent transfers reported
• 2018: 57-day hunger strike in protest of denial of medical leave and new case fabrication
• 2023–2024: Transfers between Evin, Ghezel Hesar, and Asadabad Prisons; medical furlough cut short; violent rearrest; chest injury during prison violence in February 2024
• Present: Serving life sentence in Ghezel Hesar, without medical access, furlough, or consistent family contact
Conclusion and Importance of Review
Despite legal changes enabling retrials, reductions, or release for those convicted of Moharebeh, Afshin Baymani remains in prison. His case highlights the broader plight of long-term political-security prisoners in Iran, underlining the need for both domestic and international mechanisms to review and reduce such sentences. His situation emphasizes denial of fundamental rights during imprisonment—furlough, visits, legal access—and the urgent necessity of sustained advocacy.
Urgent Needs:
• Regular, equal access to lawyer and family
• Independent medical evaluation, particularly after reports of violence and long-term health conditions
• Legal review for retrial, sentence reduction, or release under current laws
• Enforcement of prison regulations on visits, contact, and furlough
• Access to adequate healthcare and treatment
About this Series
This report is part of HRANA’s “More than Two Decades Behind Bars” series, aimed at continuously documenting long-term prisoner cases and reminding society of the collective responsibility to make their struggles visible and pursue their rights.