HRANA – Many political and religious prisoners in Iran have endured over twenty years behind bars. To prevent their cases from fading from public memory in the flow of daily news, HRANA has launched a series of reports highlighting their situations. Each installment outlines the prisoner’s legal case, detention conditions, access to rights, and immediate needs.
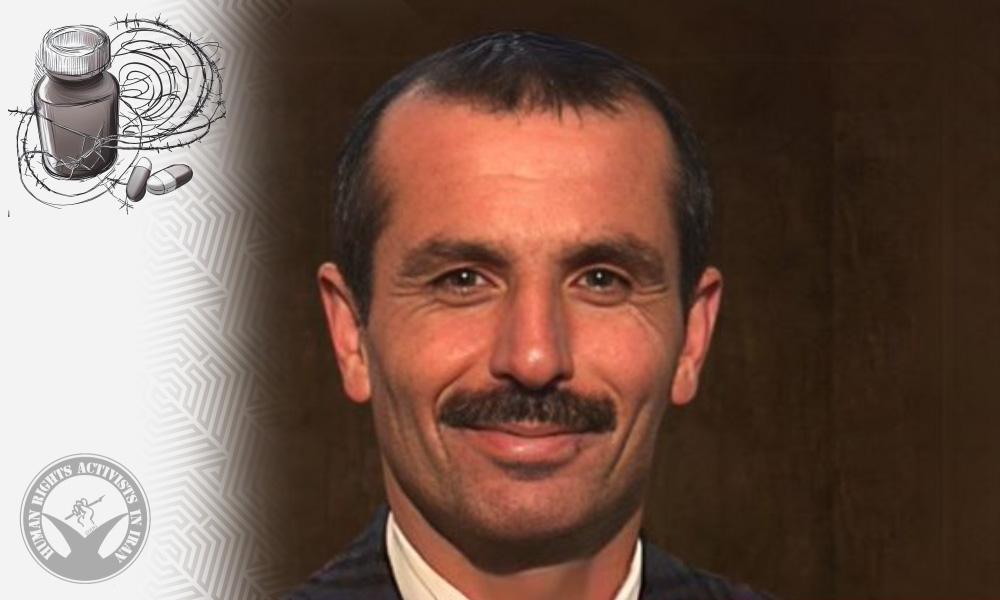
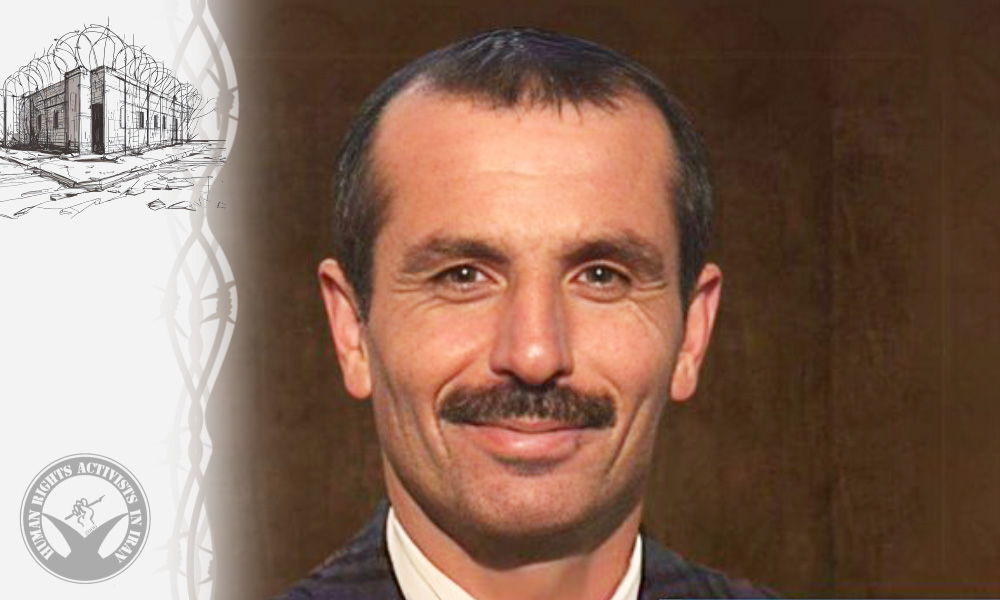
In this report, HRANA, the news arm of Human Rights Activists in Iran, examines the latest situation of Gholamhossein Kalbi after more than twenty years of imprisonment.
Information Sheet
• Name: Gholamhossein Kalbi
• Year of arrest: 2000 (1379 in the Iranian calendar)
• Charge: Moharebeh (“enmity against God”) through membership in the Mojahedin-e Khalq Organization (MEK)
• Initial sentence: Death penalty
• Current sentence: Life imprisonment (commuted with one degree of reduction)
• Places of detention: After arrest, he spent 14 months in solitary confinement at The Ministry of Intelligence’s detention facility in Ahvaz, later held in Ward 209 and then Ward 350 of Evin Prison. In October 2007, following conviction, he was transferred to Mahshahr Prison, and later to Karoon Prison in Ahvaz. After the closure of Karoon Prison in February 2016, he was moved to Sheiban Prison in Ahvaz, where he remains incarcerated to this day.
• Furlough / Access: No reports of furlough in recent years; limited access to family and lawyer.
• Current status: Still serving a life sentence, despite legal changes that could allow for review or reduction.
Case Narrative and Judicial Process
On January 8, 2001, Gholamhossein Kalbi was arrested in Dezful on charges of membership in the Mojahedin-e Khalq Organization. In 2002, the Tehran Revolutionary Court sentenced him to death on the charge of Moharebeh. His sentence was later commuted to life imprisonment. While this commutation avoided the escalation of punishment, it placed him in a category of indefinite imprisonment, which in practice can extend for decades and limit access to review mechanisms.
Key Points in the Case:
• Severe security charge: The label of Moharebeh in political-security cases in Iran is among the heaviest accusations, usually carrying wide-ranging judicial and executive consequences.
• Sentence reduction: The initial death sentence and its conversion to life imprisonment show both the gravity of the charges and the scope for judicial intervention—but do not necessarily correct potential injustices in the trial process.
• Continued imprisonment despite legal changes: Although legal reforms have made retrial, sentence reduction, or conditional release possible in some cases, Kalbi remains in prison.
Detention Conditions and Transfers
Over his decades in prison, Kalbi has been moved between several facilities. After his arrest, he spent 14 months in solitary confinement at The Ministry of Intelligence’s detention facility in Ahvaz, then was transferred to Ward 209 and later Ward 350 of Evin Prison. In October 2007, he was moved to Mahshahr Prison, where he was held for several years. Despite his family residing in Mahshahr, he was later transferred to Karoon Prison in Ahvaz. After that prison was closed, in February 2016, he was transferred to Sheiban Prison in Ahvaz, where he has been held in various wards ever since.
In July 2021, after protesting prison conditions, officials at Sheiban Prison punished him by binding his hands and feet and leaving him for hours under the scorching sun. He was then transferred to a ward worse than the previous one, prompting him to go on hunger strike.
In April 2024, he was placed in Ward 5 of Sheiban Prison without regard for the principle of separation of crimes. Later, in November 2024, he was transferred to the prison’s security ward, under overcrowded conditions without adequate space for walking. He remains there today.
Observations on Standards of Detention
• Repeated transfers: Frequent movements between wards and prisons disrupt access to family, lawyer, and medical care.
• Solitary confinement as punishment: Kalbi spent 14 months in solitary confinement at The Ministry of Intelligence’s detention facility in Ahvaz. International standards require solitary confinement to be exceptional, time-limited, and supervised.
• Exposure to violence: Reports document both physical and verbal abuse during his imprisonment in Sheiban Prison. Notably, in July 2021, he was tied up and left under extreme heat as punishment for protesting prison conditions. Such incidents highlight the need for independent documentation and legal accountability.
• Medical neglect: Despite suffering from heart disease, hernia, dental infections, jaw and gum problems, spinal and neck arthritis, fungal infection leading to severe toenail disease, high cholesterol, chronic ear infection with hearing loss, Kalbi has consistently been denied transfer to hospitals or specialized treatment. “Access to medical care” is a fundamental right recognized in Iranian law, international treaties, and human rights standards. Systematic denial of medical care constitutes inhuman treatment and violates both the right to health and, in some cases, the right to life, often being used as an instrument of coercion and repression.
Access to Family, Lawyer, and Furlough
In recent years, Kalbi has not been granted furlough. His access to his family and lawyer has been reported as limited. These restrictions not only have psychological and social consequences but also undermine his ability to mount an effective legal defense or pursue retrial mechanisms.
Potential Legal Remedies (General Recommendations)
1. Retrial: Based on new evidence or substantive/procedural flaws in the original ruling.
2. Sentence reduction or conversion: If legal grounds exist.
3. Conditional release / suspension of sentence: Subject to conditions such as time served, good behavior, or health status.
4. Redress for rights violations during detention: Including access to healthcare, protection from violence, and regular visits.
5. International advocacy and documentation: If domestic remedies are blocked, use of international reporting and human rights mechanisms.
Summary Timeline
• 2001: Arrest; charge of Moharebeh through MEK membership.
• Initial sentence: Death; commuted to life imprisonment.
• Post-arrest: 14 months in solitary at The Ministry of Intelligence’s detention facility in Ahvaz, then Ward 209 and 350 of Evin.
• 2007 (1386): Transferred to Mahshahr Prison.
• 2016 (1394): Transferred to Sheiban Prison in Ahvaz.
• July 2021 (Tir 1400): Punitive torture reported—hands and feet tied, left for hours under scorching sun.
• April 2024 (Farvardin 1403): Moved to Ward 5 of Sheiban Prison without separation of crimes.
• November 2024 (Aban 1403): Transferred to security ward of Sheiban Prison.
• Recent years: No furlough, denial of medical care, restricted access to family and lawyer.
• Current status: Serving life sentence despite potential legal changes allowing review.
Conclusion and Importance of Case Review
Despite legal changes that allow retrials, sentence reductions, or conditional release for those convicted of Moharebeh, Kalbi remains imprisoned. His case illustrates the plight of long-term political-security prisoners in Iran, whose files deserve review as a crucial step toward freedom and justice.
His situation highlights both the denial of fundamental rights during detention (furlough, visits, legal representation) and the urgent need to use all domestic and international legal mechanisms for review and reduction of such lengthy sentences.
Urgent Needs
• Regular, non-discriminatory access to lawyer and family.
• Independent medical evaluation, especially regarding torture allegations and chronic illnesses.
• Consideration for retrial or other legal remedies for sentence reduction/termination under current laws.
• Enforcement of prison regulations regarding calls, visits, and furlough.
• Adequate medical services and treatment.
About this Series
This report is part of the “Two Decades Behind Bars” series, which aims to document the cases of long-term prisoners and to highlight the collective responsibility to ensure their visibility and pursue their rights.