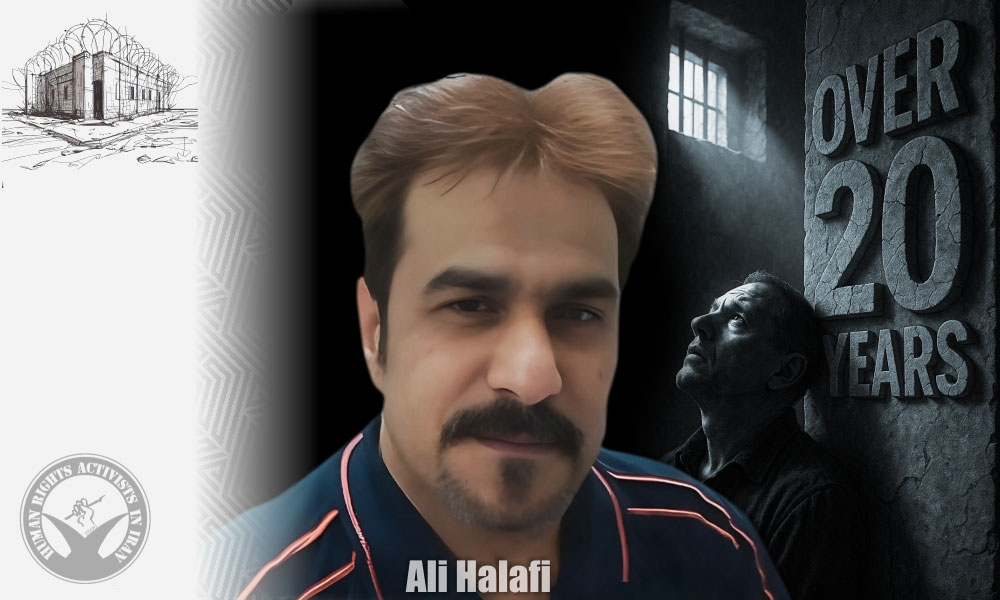
HRANA – A large number of political prisoners and the prisoners of conscience have spent more than two decades of their lives in Iran’s prisons. To ensure their names are not forgotten amid daily news cycles, HRANA is publishing a series introducing these prisoners and their conditions. Each report reviews their judicial case, detention situation, access rights, and urgent needs.
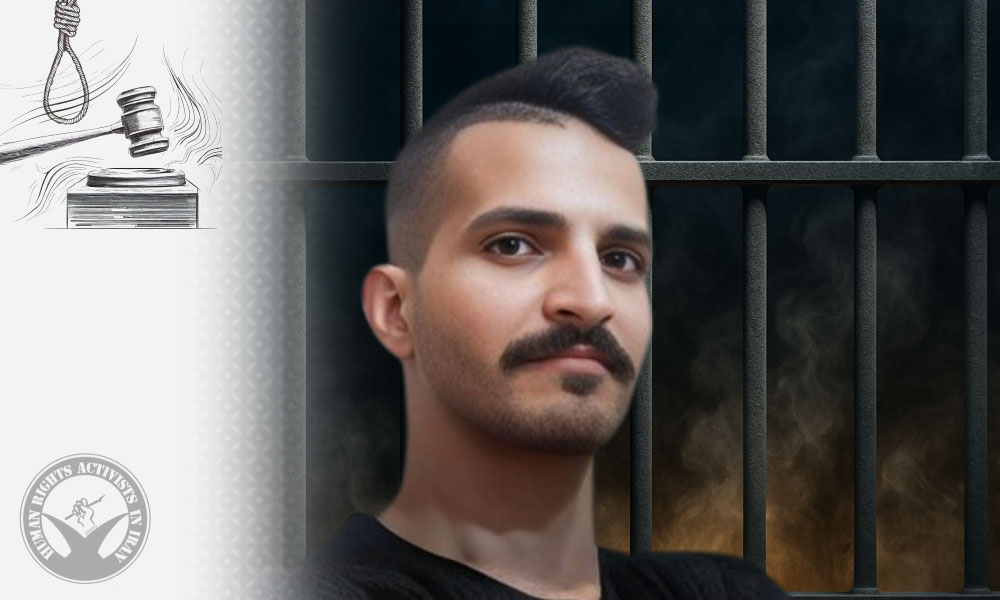
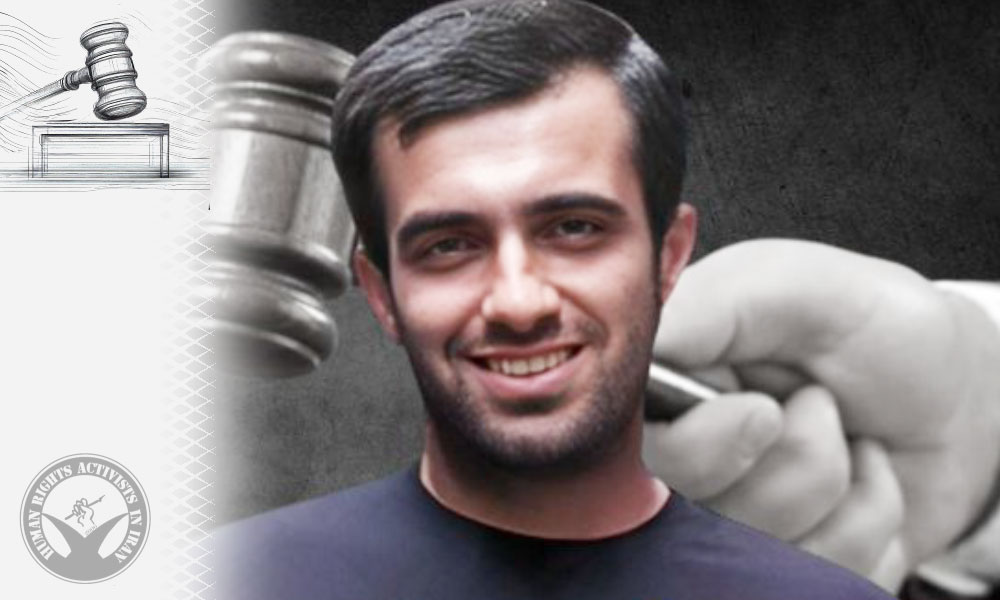
In this report, HRANA, the news agency of Human Rights Activists in Iran, examines the latest situation of Hamzeh Sawari Laftah after two decades of imprisonment.
Information Summary
• Name: Hamzeh Savari Leftah
• Year of Arrest: 2005 (1384 SH)
• Charges Announced: “Corruption on Earth (efsad fel-arz), moharebeh (enmity against God), and acting against national security”
• Initial Sentence: Death penalty
• Current Sentence: Life imprisonment (reduced by one degree)
• Places of Detention: Three months in Sheiban Prison (Ahvaz), eight years in Karun Prison (Ahvaz), transferred to Rajai Shahr Prison (Karaj) until 2023, held in Ward 8 of Evin Prison in August 2023, transferred to Ghezel Hesar Prison (Karaj) in September 2023 where he remains.
• Leave/Access: No furlough reported in recent years; limited access to family and lawyer.
• Current Status: Still serving a life sentence despite legal changes that could allow for review or reduction.
Case History and Judicial Process
On September 2, 2005, at the age of just sixteen, Hamzeh Sawari was arrested by security forces. He was sentenced to death by the Ahvaz Revolutionary Court on charges of “corruption on Earth, moharebeh, and acting against national security.” The sentence was later commuted to life imprisonment. While this change prevented the implementation of the death penalty, it placed him among those condemned to indefinite imprisonment – effectively a punishment that can last for decades and severely limits the possibility of judicial review.
Key points in the process:
• Heavy security charge: The label of “moharebeh” is among the most severe accusations in Iran’s political-security cases, carrying extensive judicial and executive consequences.
• Sentence reduction: The initial death penalty, later converted to life imprisonment, illustrates both the severity of the charges and the possibility of judicial intervention, but does not necessarily mean injustices in the process were remedied.
• Ongoing imprisonment despite legal changes: Although legal reforms could allow for retrial, reduced sentences, or conditional release, Sawari remains in prison.
Detention Conditions and Transfers
Throughout his imprisonment, Hamzeh Savari has been held in multiple prisons: eight years in Karun Prison (Ahvaz), three months in Sheiban Prison (Ahvaz), then transferred to Rajai Shahr Prison (Karaj). In 2014, he was held in Hall 12 of Rajai Shahr, and in 2017 he was violently moved to Ward 10 (Unit 4) of the same prison.
In August 2023, he was transferred to Ward 8 of Evin Prison, but after one month, he was moved to the security unit (Ward 3) of Ghezel Hesar Prison (Karaj). He staged a hunger strike in protest of these transfers and spent some time in solitary confinement. He has remained in Ghezel Hesar since then.
Observations Related to Detention Standards
• Frequent transfers: Repeated relocations between wards and prisons disrupt access to family, legal counsel, and medical care.
• Solitary confinement as punishment: After arrest, Sawari spent nine months in solitary confinement in The Ministry of Intelligence’s detention facilities in Ahvaz and Shiraz. He was repeatedly placed in solitary confinement during his years in Karun Prison. He was again sent to solitary in 2017 after protesting his transfer to Ward 10 of Rajai Shahr, in September 2023 after objecting to being moved from Evin to Ghezel Hesar, and once more in August 2025. Such practices conflict with international standards, where solitary confinement must be exceptional, limited, and supervised.
• Exposure to violence in prison: Reports document physical and verbal abuse during his eight years in Karun Prison. In August 2017, he was beaten after being moved from Hall 12 to Ward 10 of Rajai Shahr. In September 2023, he was subjected to violence during his forced transfer from Evin to Ghezel Hesar. In August 2025, following his protest against the transfer of political prisoner Saeed Masouri to Zahedan Prison and the executions of Behrouz Ehsani Eslamloo and Mehdi Hassani, he and several other prisoners were beaten by Ghezel Hesar’s special guard unit. These incidents underscore the need for independent documentation and legal follow-up.
• Deprivation of medical care: Despite suffering from heart disease, lung inflammation, a torn cruciate ligament in his right knee with severe Baker’s cyst, chronic stomach pain, cervical arthritis, and needing spinal surgery, Sawari has been consistently denied hospital transfers and specialist treatment. Denying prisoners access to medical care constitutes inhuman treatment and violates both the right to health and the right to life, often used as a tool of pressure and suppression.
Access to Family, Lawyer, and Leave
In recent years, Sawari has not been granted furlough, and his access to family and lawyer remains limited. These restrictions not only harm his social and psychological well-being but also undermine his ability to mount an effective defense and pursue retrial options.
Potential Legal Avenues (General Recommendations)
1. Retrial (E’adeye Dadrasi): Assessing new evidence or substantive/procedural flaws.
2. Sentence reduction/commutation: If legal grounds are available.
3. Conditional release/suspension: Evaluating eligibility based on time served, conduct, and health.
4. Pursuing rights violations during imprisonment: Including denial of medical care, exposure to violence, lack of visitation, and restricted access to legal counsel.
5. International documentation and advocacy: Turning to human rights mechanisms if domestic remedies are blocked.
Timeline Summary
• 2005 (1384): Arrested at age 16 on charges of “corruption on Earth, moharebeh, and acting against national security.”
• Initial Sentence: Death penalty, later commuted to life imprisonment.
• Post-conviction: Eight years in Karun Prison.
• 2014 (1393): Held in Hall 12 of Rajai Shahr Prison (Karaj).
• 2017 (1396): Beaten; transferred to Ward 10 of Rajai Shahr.
• August 2023 (Mordad 1402): Transferred to Ward 8 of Evin Prison.
• September 2023 (Shahrivar 1402): Violently transferred to Ghezel Hesar; solitary confinement.
• August 2025 (Mordad 1404): Beaten and placed in solitary again in Ghezel Hesar.
• Recent years: No furlough, denied medical care, restricted family and lawyer visits.
• Current status: Life sentence continues despite legal reforms that could allow for review.
Conclusion and Importance of Review
Despite legal changes enabling retrial, reduced sentences, or conditional release for those convicted of moharebeh, Hamzeh Sowari remains imprisoned. His case exemplifies the situation of long-term political-security prisoners in Iran whose cases require urgent review.
It highlights both the denial of fundamental rights during imprisonment (furlough, visits, legal counsel) and the necessity of using all possible domestic and international legal mechanisms to reduce sentences and secure release.
Urgent Needs
• Regular and non-discriminatory access to family and lawyer.
• Independent medical evaluation in cases of alleged abuse or long-term conditions.
• Examination of the possibility of retrial or other mechanisms for reducing/suspending the sentence under updated laws.
• Enforcement of prison regulations regarding contact, visitation, and furlough.
• Access to adequate medical care and treatment.
About this Series
This report is part of the “More than Two Decades behind Bars” series, which aims to document the cases of long-term prisoners and to highlight the collective responsibility to ensure their visibility and pursue their rights.